Introduction
Pipeline expansion is an evaluation of the pipeline in-place analysis to determine maximum pipeline expansion at the two terminations and the maximum associated axial load in the pipeline. Both results are used in managing the expansion of the pipeline in end expansions spools design, global buckling (lateral and upheaval buckling), and pipeline walking analysis.
Notable Projects
Project Name |
Project Number |
Notes |
West DON & DON South West |
KW 1009 |
|
Codes & Standards
Company |
Title |
Doc Number / Date |
DNV |
Submarine Pipeline Systems (Strain Based Limit State) |
DNV-OS-F101 |
Course Notes
Author |
Title |
Notes |
C. Sicilia |
Lateral Buckling Assessment and Mitigation Design |
|
Trevor Gee IBC |
Pipeline Course |
Books
Author |
Title |
Chapter |
Young Bai |
Pipelines and risers |
|
Pipeline Expansion

Basic Formula
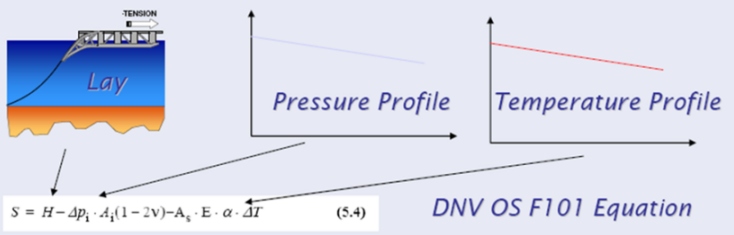
The effective axial force that determines the global response of a pipeline is denoted S. Counting tensile force as positive:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Where:
S = Effective axial force
N = Steel force
H = Effective (residual) lay tension
Δpi = Internal pressure difference relative to as laid
ΔΤ = Temperature difference relative to as laid
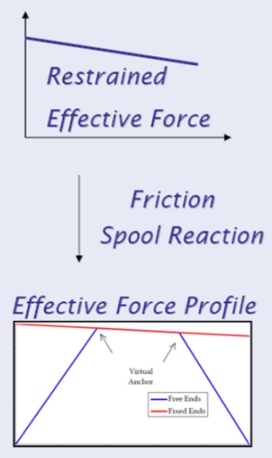
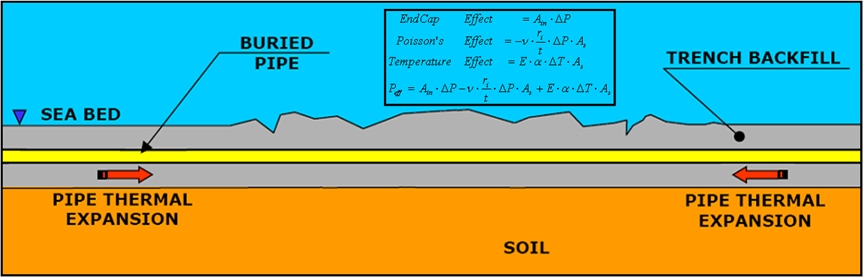
If a pipeline is buried and operates at a temperature higher than the temperature during installation, it wants to expand axially due to internal pressure and temperature changes, but is restrained by the surrounding soil friction and so compressive loads are generated.
The thermal expansion analysis is not simple and FEA (finite element analysis) tools are commonly used to design mitigation of thermal expansion problems. Snaking (lateral displacement) or upheaval buckling (vertical displacement) can occur due to excessive elongation, or the pipeline may experience walking (pipeline walking).